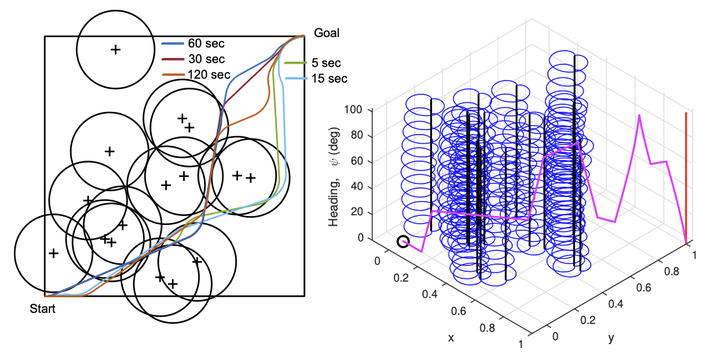
Abstract
Existing methods for avoiding dynamic engagement zones (EZs) and minimizing risk leverage the calculus of variations to obtain optimal paths. While such methods are deterministic, they scale poorly as the number of engagement zones increases. Furthermore, optimal-control based strategies are sensitive to initial guesses and often converge to local, rather than global, minima. This paper presents a novel sampling-based approach to obtain a feasible flight plan for a Dubins vehicle to reach a desired location in a bounded operating region in the presence of a large number of engagement zones. The dynamic EZs are coupled to the vehicle dynamics through its heading angle. Thus, the dynamic two-dimensional obstacles in the (x,y) plane can be transformed into three-dimensional static obstacles in a lifted (x,y,ψ) space. This insight is leveraged in the formulation of a Rapidly-exploring Random Tree (RRT*) algorithm. The algorithm is evaluated with a Monte Carlo experiment that randomizes EZ locations to characterize the success rate and average path length as a function of the number of EZs and as the computation time made available to the planner is increased.